App 的本质和 Mach-O 文件
进程
App 的本质是一个可执行程序,是一段计算机代码和数据的集合。从操作系统的角度来看,App 的本质是一个进程。进程是计算机中正在运行的程序的实例。在操作系统中,进程是操作系统分配资源和调度执行的基本单位。每个进程都有自己的内存空间、寄存器集合、文件句柄、网络连接等资源,它们可以独立地运行和被管理。
进程是操作系统中最基本的资源分配和调度单位。操作系统通过进程控制块 PCB(Process Control Block) 来管理进程,PCB 包含了进程的状态、进程 ID、进程优先级、内存使用情况、文件句柄等信息。当操作系统需要切换到另一个进程时,它会保存当前进程的上下文,然后加载另一个进程的上下文,从而实现进程之间的切换。
在 macOS 中,PCB 被称为 proc。proc 结构体是 macOS 内核中非常重要的数据结构,用于描述进程在内核中的状态和信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
struct proc {
LIST_ENTRY(proc) p_list; /* List of all processes. */
void * XNU_PTRAUTH_SIGNED_PTR("proc.task") task; /* corresponding task (static)*/
struct proc * XNU_PTRAUTH_SIGNED_PTR("proc.p_pptr") p_pptr; /* Pointer to parent process.(LL) */
pid_t p_ppid; /* process's parent pid number */
pid_t p_original_ppid; /* process's original parent pid number, doesn't change if reparented */
pid_t p_pgrpid; /* process group id of the process (LL)*/
uid_t p_uid;
gid_t p_gid;
uid_t p_ruid;
gid_t p_rgid;
uid_t p_svuid;
gid_t p_svgid;
uint64_t p_uniqueid; /* process unique ID - incremented on fork/spawn/vfork, remains same across exec. */
uint64_t p_puniqueid; /* parent's unique ID - set on fork/spawn/vfork, doesn't change if reparented. */
lck_mtx_t p_mlock; /* mutex lock for proc */
pid_t p_pid; /* Process identifier. (static)*/
char p_stat; /* S* process status. (PL)*/
char p_shutdownstate;
char p_kdebug; /* P_KDEBUG eq (CC)*/
char p_btrace; /* P_BTRACE eq (CC)*/
/* 以下其他字段已省略 */
};
proc 包含了大量的字段和指针,用于描述进程的各种属性和资源使用情况,例如进程状态(p_stat)、进程 ID(p_pid)、进程名称(p_comm)、进程优先级(p_priority)、进程内存使用情况(p_vmspace)、文件描述符表(p_fd)、线程列表(p_threadlist)等。
Mach-O 文件
在 App 加载到内存成为进程之前,macOS 上的可执行文件是 Mach-O 文件。Mach-O 文件包含了可执行代码、数据、符号表、动态链接信息等多个部分,是 macOS 中应用程序和库文件的基本格式。
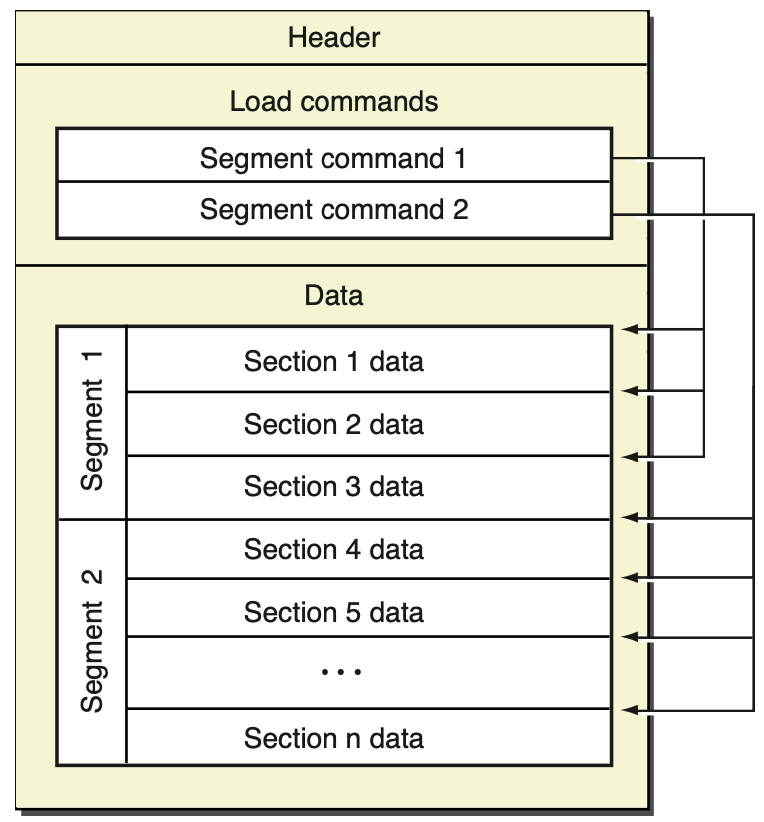
Mach-O 文件的格式可以分为文件头(Header)、加载命令(Load commands)和数据区(Raw segment data)三个部分。
包含多个 CPU 架构的 Mach-O 文件被称为 Fat Binary。可以通过 file 命令查看 Mach-O 文件的 CPU 架构。
1
2
3
4
$ file /System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator
/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [x86_64:Mach-O 64-bit executable x86_64] [arm64e:Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64e]
/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator (for architecture x86_64): Mach-O 64-bit executable x86_64
/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator (for architecture arm64e): Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64e
Fat Binary 对应的 fat_header 在操作系统中的数据结构定义是 fat_header。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
struct fat_header {
uint32_t magic; /* FAT_MAGIC */
uint32_t nfat_arch; /* number of structs that follow */
};
// Fat Binary 包含了多个 fat_arch 组成的 Mach-O 文件
struct fat_arch {
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier (int) */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier (int) */
uint32_t offset; /* file offset to this object file */
uint32_t size; /* size of this object file */
uint32_t align; /* alignment as a power of 2 */
};
可以看到,macOS 系统的计算器程序 Mach-O 文件,是包含了 x86_64 和 arm64e 两种 CPU 架构的 Fat Binary。
iOS 系统自 iOS 11.0 版本以后,不再支持
armv7,armv7s等架构,只支持arm64架构。所以仅支持iOS 11.0以后版本的项目,打包产物的Fat Binary只有arm64架构的Mach-O文件。这也是Xcode 14.0取消了bitcode的原因,因为不再需要编译成bitcode中间产物,且bitcode转译会消耗 AppStore 的服务器资源
文件头(haeder)
Mach-O 文件头包含了文件类型、CPU 类型、加载命令数量等信息。Mach-O 文件支持多种文件类型,包括可执行文件、动态链接库、框架等。CPU 类型指定了可执行文件适用的 CPU 架构,例如 x86、x86_64、armv7、arm64 等。加载命令数量指定了文件中包含的加载命令数量。
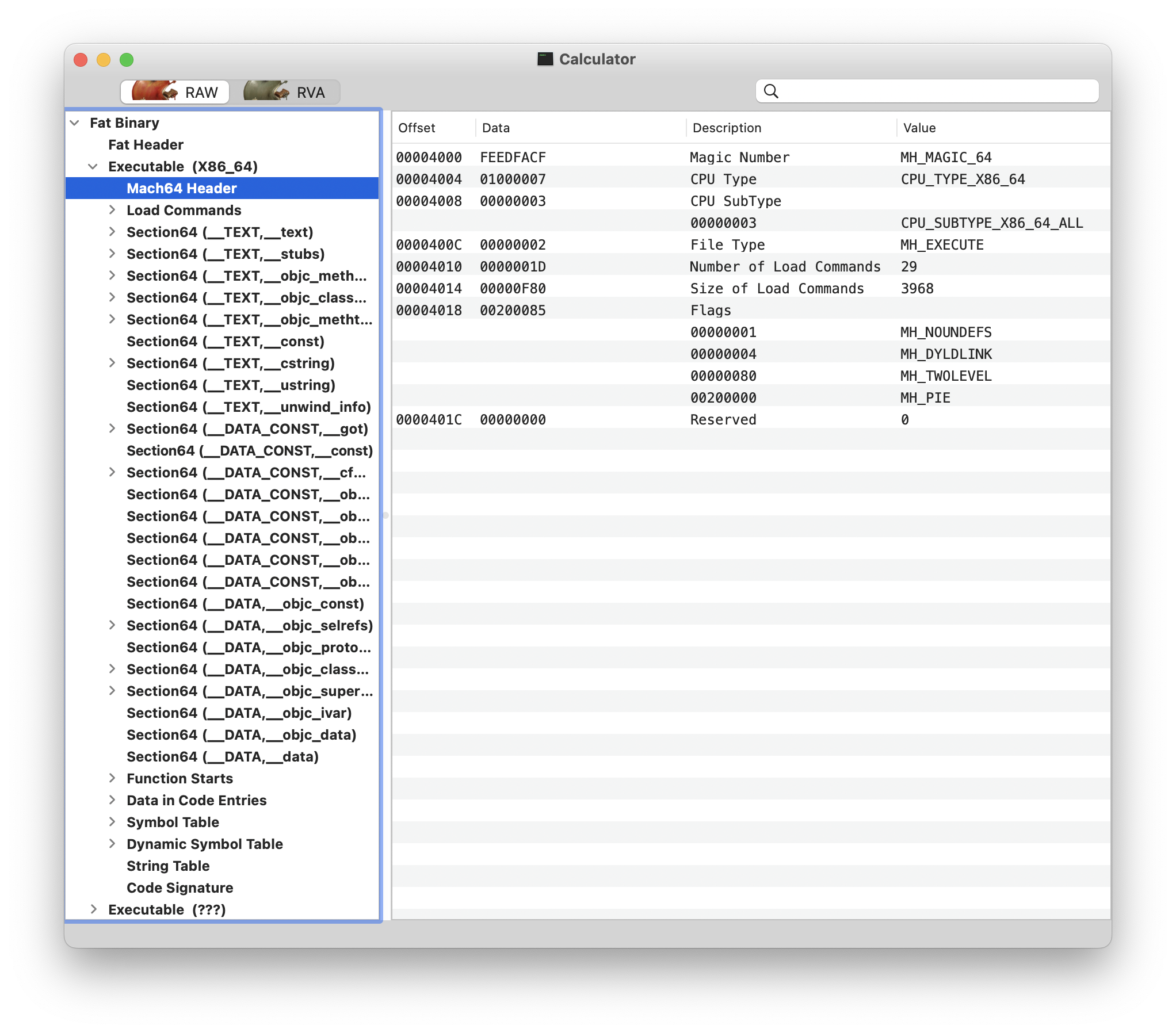
otool 命令是 macOS 和 iOS 等操作系统上的一个工具,用于查看可执行文件、动态库和框架等二进制文件的信息。它可以用来查看二进制文件的头部信息、节表、符号表、动态链接信息等。
1
2
3
4
5
$ otool -h /System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator
/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator:
Mach header
magic cputype cpusubtype caps filetype ncmds sizeofcmds flags
0xfeedfacf 16777228 2 0x80 2 29 4208 0x00200085
除了 otools 命令,还可以使用 MachOView 工具通过图形化页面来查看 Mach-O 文件
1
brew install machoview
Fat Binary 中,每个架构都有一个 header 文件头,被称为 mach_header。64 位架构的 mach_header 会多一个保留字段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
/*
* The 32-bit mach header appears at the very beginning of the object file for
* 32-bit architectures.
*/
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
/* Constant for the magic field of the mach_header (32-bit architectures) */
#define MH_MAGIC 0xfeedface /* the mach magic number */
#define MH_CIGAM 0xcefaedfe /* NXSwapInt(MH_MAGIC) */
/*
* The 64-bit mach header appears at the very beginning of object files for
* 64-bit architectures.
*/
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */
};
/* Constant for the magic field of the mach_header_64 (64-bit architectures) */
#define MH_MAGIC_64 0xfeedfacf /* the 64-bit mach magic number */
#define MH_CIGAM_64 0xcffaedfe /* NXSwapInt(MH_MAGIC_64) */
加载命令(Load commands)
Mach-O 文件中的加载命令(Load Command)用于描述可执行文件的各个段的属性和位置等信息,操作系统会根据这些信息将可执行文件加载到内存中。每个 Load Command 描述了一个特定的段或区域。常见的 Load Command 包括:
LC_SEGMENT和LC_SEGMENT_64:描述可执行代码和数据的段信息;LC_SYMTAB和LC_DYSYMTAB:描述符号表和动态符号表信息;LC_LOAD_DYLIB和LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB:描述动态链接库的信息;LC_MAIN:描述程序入口点的信息。
1
2
3
4
struct load_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* type of load command */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* total size of command in bytes */
};
数据区(Raw segment data)
Mach-O 文件的数据区包含了多个段(Segment),每个段包含了不同类型的数据。常见的段包括 __TEXT、__DATA、__LINKEDIT 等。其中,__TEXT 段包含了代码和只读数据,__DATA 段包含了全局变量和静态变量等数据,__LINKEDIT 段包含了符号表和重定位信息等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
struct segment_command_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT_64 */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section_64 structs */
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint64_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment */
uint64_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint64_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint64_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
int32_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
int32_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
在 Mach-O 文件中,每个 Segment 包含一个或多个 section,每个 section 包含了一组相关的数据或代码。例如,在一个可执行文件中,常见的 Segment 包括 __TEXT、__DATA、__LINKEDIT 等,每个 Segment 包含了多个 section,例如 __TEXT 包含了 __text、__cstring、__stub 等多个 section。
Section 是 Mach-O 文件中的一个子单元,它是 Segment 中的一个子段,包含了一组相关的数据或代码。每个 Section 都有一个名称和一个类型,例如 __text、__data、__cstring 等。在 Mach-O 文件中,Section 的名称和类型通常与编译器和链接器相关,不同的编译器和链接器可能会使用不同的名称和类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
struct section_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
char sectname[16]; /* name of this section */
char segname[16]; /* segment this section goes in */
uint64_t addr; /* memory address of this section */
uint64_t size; /* size in bytes of this section */
uint32_t offset; /* file offset of this section */
uint32_t align; /* section alignment (power of 2) */
uint32_t reloff; /* file offset of relocation entries */
uint32_t nreloc; /* number of relocation entries */
uint32_t flags; /* flags (section type and attributes)*/
uint32_t reserved1; /* reserved (for offset or index) */
uint32_t reserved2; /* reserved (for count or sizeof) */
uint32_t reserved3; /* reserved */
};
参考资料