一道算法综合题
题目描述
You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1) (i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a route that requires the minimum effort.
A route’s effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route.
Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
- Example 1:
1
2
3
4
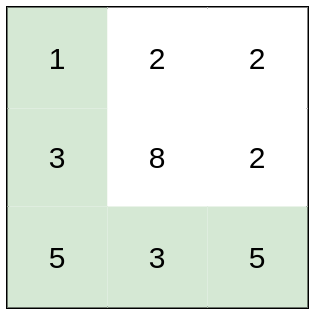
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells.
This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Binary Search
DFS/BFS 判断给定 threshold 是否可行,二分搜索确定最小值。
BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
class Solution {
private:
int m, n;
int dir[4][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0} };
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
m = heights.size();
n = m > 0 ? heights[0].size() : 0;
int left = 0, right = 10e6;
int res = -1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
bool reachable = bfs(heights, mid);
if (reachable) {
res = mid;
right = mid - 1;
}else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
bool bfs(vector<vector<int>> &heights, int limit) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({0, 0});
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
vis[0][0] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front().first, y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int new_x = x + dir[i][0];
int new_y = y + dir[i][1];
if (new_x >= 0 && new_y >= 0 && new_x < m && new_y < n && !vis[new_x][new_y] && abs(heights[new_x][new_y] - heights[x][y]) <= limit) {
q.push({new_x, new_y});
vis[new_x][new_y] = true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
DFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
class Solution {
private:
int m, n;
int dir[4][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0} };
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
m = heights.size();
n = m > 0 ? heights[0].size() : 0;
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
int left = 0, right = 10e6;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
std::fill(vis[i].begin(), vis[i].end(), false);
}
dfs(heights, 0, 0, mid, vis);
if (vis[m - 1][n - 1]) {
right = mid;
}else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>> &heights, int x, int y, int threshold, vector<vector<bool>> &vis) {
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= m || y >= n || vis[x][y]) {
return;
}
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int new_x = x + dir[i][0];
int new_y = y + dir[i][1];
if (new_x < 0 || new_y < 0 || new_x >= m || new_y >= n || vis[new_x][new_y]) {
continue;
}
if (abs(heights[new_x][new_y] - heights[x][y]) > threshold) {
continue;
}
dfs(heights, new_x, new_y, threshold, vis);
}
}
};
UnionFind
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
class UnionFind {
private:
vector<int> pa;
int count;
public:
UnionFind(int n):pa(n), count(n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pa[i] = i;
}
}
int root(int x) {
return x == pa[x] ? x : pa[x] = root(pa[x]);
}
void uni(int x, int y) {
int px = root(x);
int py = root(y);
if (px != py) {
pa[px] = py;
count--;
}
}
bool connected(int x, int y) {
return root(x) == root(y);
}
};
struct Edge {
int x, y;
int d;
Edge(int _x, int _y, int _d): x(_x), y(_y), d(_d) {};
bool operator < (const Edge &other) const {
return d > other.d;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
priority_queue<Edge> edges;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int id = i * n + j;
if (i > 0) {
edges.push(Edge(id - n, id, abs(heights[i][j] - heights[i - 1][j])));
}
if (j > 0) {
edges.push(Edge(id - 1, id, abs(heights[i][j] - heights[i][j - 1])));
}
}
}
UnionFind uf(m * n);
int res = 0;
while (!edges.empty()) {
Edge e = edges.top();
edges.pop();
uf.uni(e.x, e.y);
if (uf.connected(0, m * n - 1)) {
res = e.d;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
};
Dijkstra
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
struct Node {
int x, y;
int limit;
Node(int _x, int _y, int _limit) : x(_x), y(_y), limit(_limit) {}
bool operator < (const Node &other) const {
return limit > other.limit;
}
};
class Solution {
private:
int dirs[4][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0} };
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int m = heights.size(), n = m > 0 ? heights[0].size() : 0;
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
priority_queue<Node> pq;
pq.emplace(Node(0, 0, 0));
vector<int> dist(m * n, INT_MAX);
dist[0] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
Node node = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int x = node.x, y = node.y, limit = node.limit;
if (vis[x][y]) {
continue;
}
if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) {
break;
}
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dirs[i][0];
int ny = y + dirs[i][1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) {
continue;
}
int new_limit = max(limit, abs(heights[nx][ny] - heights[x][y]));
if (new_limit >= dist[nx * n + ny]) {
continue;
}
dist[nx * n + ny] = new_limit;
pq.emplace(Node(nx, ny, new_limit));
}
}
return dist.back();
}
};
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.